wolfBoot 2.3.0 has finally been released! The universal secure bootloader extends its support to new platforms, improves existing ports, and introduces new groundbreaking features that set the pace to defining secure-boot for the next generation of embedded systems.
A New Era of Secure Boot with ML-DSA and Hybrid Authentication
The introduction of quantum resistant algorithms in the latest releases of wolfSSL has accelerated the integration of asymmetric cryptography in our secure boot solution. In 2023, wolfBoot v2.0.0 expanded its signature verification algorithms to include the hash-based stateful signatures LMS (+HSS) and XMSS (^MT). wolfBoot v2.3.0 further extends these options by introducing ML-DSA, as specified in FIPS-204, for verifying the authenticity of firmware and other critical components. Support for ML-DSA in wolfBoot is currently available in three variants: ML-DSA-44, ML-DSA-65 and ML-DSA-87, corresponding to NIST security category 2, 3 and 5, respectively.
Hybrid Authentication: Post-Quantum Meets Classic Cryptography
One of the most anticipated features in WolfBoot 2.3.0 is its support for hybrid authentication, a method that combines Post-Quantum Cryptography (PQC) algorithms with traditional cryptographic techniques like ECC and RSA. This hybrid approach strengthens security by combining the resilience of PQC, which resists quantum attacks, with the well-established reliability of classic algorithms. Pairing PQC algorithms with ECC521 offers a path toward CNSA 2.0 compliance, a set of guidelines for systems demanding the highest levels of security.
Hybrid authentication in WolfBoot secures the boot process by signing and validating boot images with a combination of PQC and traditional cryptography. This dual-layer protection approach ensures that even if one algorithm becomes vulnerable, the other remains resilient, offering a future-proof strategy for embedded systems as quantum computing capabilities grow.
Boot time optimization and performance monitoring
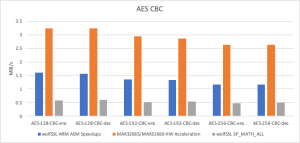
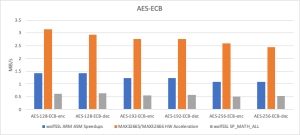
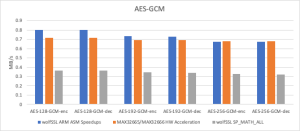
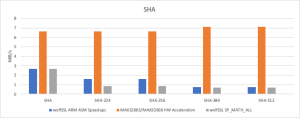
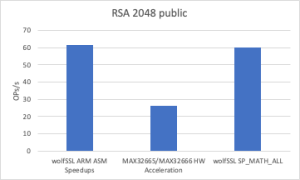
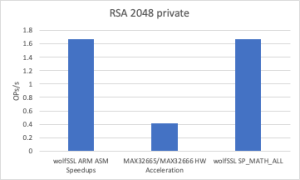
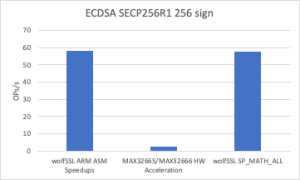
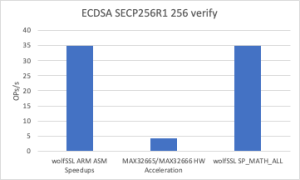
Thanks to the newly introduced assembly optimization for ARM in wolfCrypt, image verification times have been dramatically reduced. These ARM optimizations are now enabled by default on all Cortex-M devices.
New benchmark tools have been added to our continuous integration environment, to ensure that we can constantly monitor boot time, footprint size, runtime memory usage and other performance indicators.
Improved keystore and keyvault management
Starting with wolfBoot 2.3.0, it is now possible to store public keys of different sizes in the same trust anchor. This is a crucial feature to allow double signature verification in hybrid mode, or when integrating heterogeneous components in the boot chain, involving more than one cipher at a time.
PKCS11 key vault storage drivers have also been improved, and can now reliably store keys in non-volatile memories, ensuring compatibility with wolfPKCS11.
Hardware support
In this version, the following new targets have been added to the list of hardware platforms we support:
- Infineon AURIX TriCore TC3xx
- Microchip AT-SAMA5D3
- Nordic nRF5340
Moreover, the support for some of the existing ports has been improved and stabilized. During the development of wolfBoot v. 2.3.0 we mostly worked on the following targets:
- NXP i.MX-RT family: the capabilities have been extended, including the support for built-in High-Assurance Boot (HAB) mechanism, provided by the manufacturer. Flash interaction has improved, and DCACHE invalidation has been fine-tuned to increase performance
- Renesas RX: improvements introduced for this family of microcontrollers include the introduction of a full-flash erase operation, a more efficient flash management and support for boot-time IRQ.
- Raspberry Pi: added UART driver
Find out more about wolfBoot
Join our webinar “What’s new in wolfBoot” on November 21, 2024 to discover more details about wolfBoot 2.3.0 and our real-life scenarios for post-quantum cryptography adoption.
If you want to share your secure-boot experience with us or ask us anything on this topic, reach out via email at facts@wolfSSL.com or call us at +1 425 245 8247.
Download wolfSSL Now